[빅데이터와 정보검색] 11주차 LangChain, LangGraph를 이용한 AgenticRAG 개발
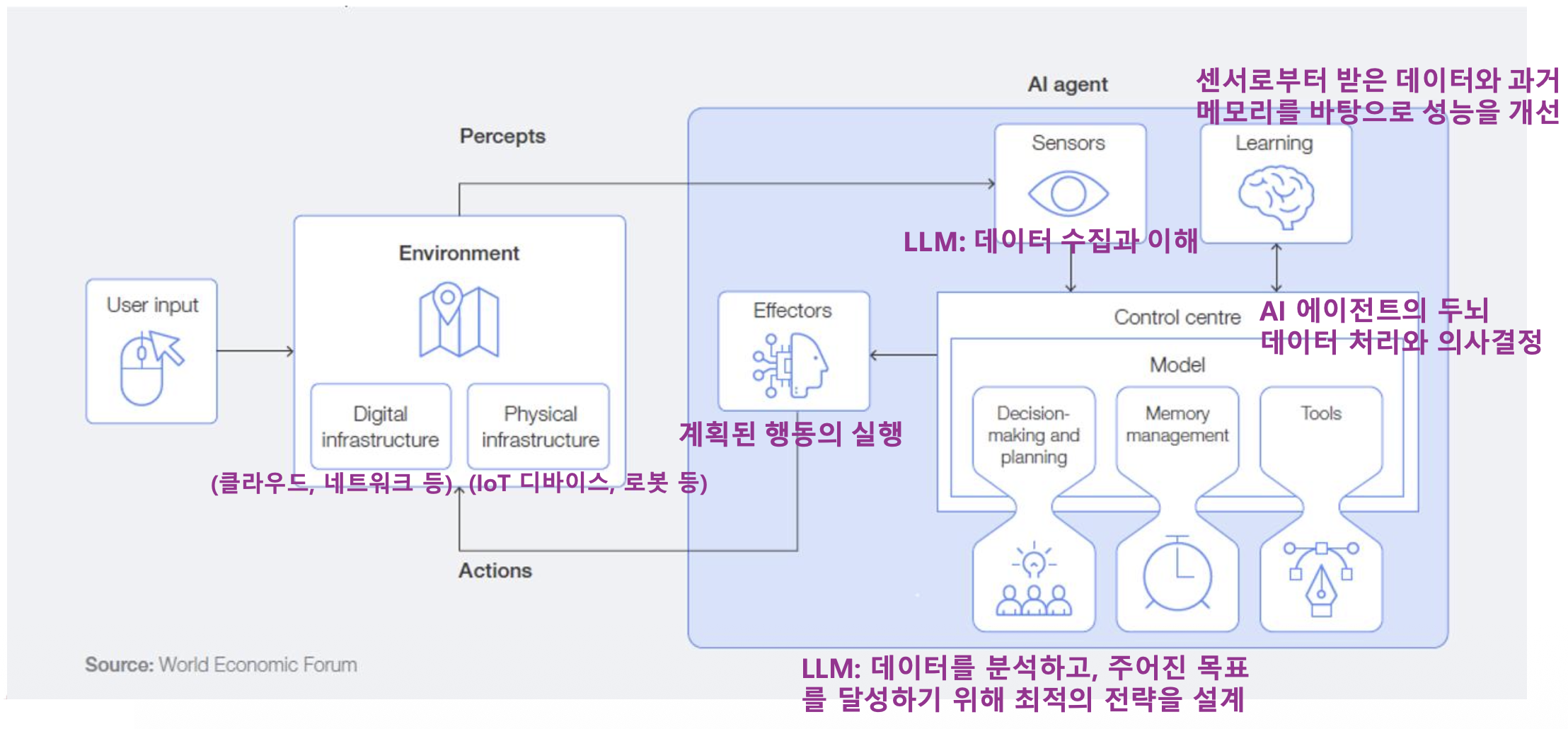
p4. AI 에이전트 아키텍처
AI 에이전트는 환경(Environment), 센서(Sensors), 학습(Learning), 컨트롤 센터(Control Centre),
실행기(Effectors) 로 구성된 구조를 통해 사용자의 요구와 환경 변화에 적응하며 자율적으로 작동
p4. AI 에이전트의 핵심 요소기술
- LLM (Large Language Model)
- 에이전트의 중앙 의사 결정자 및 추론 엔진 역할을 수행
- 추론 (Reasoning) 및 계획 (Planning)
- 복잡한 목표 달성을 위해 필요한 단계들을 스스로 생각하고 계획하는 능력
- 추론: 에이전트가 주어진 정보(프롬프트, 검색 결과, 지식베이스)를 바탕으로 논리적 결론을 도출하거나 문제 해결을 위한 아이디어를 생성
- 계획: 추론을 통해 도출된 아이디어나 목표를 달성하기 위해 필요한 구체적이고 순차적인 행동 단계(Steps)를 수립
- 복잡한 목표 달성을 위해 필요한 단계들을 스스로 생각하고 계획하는 능력
- 도구 사용 (Tool Use / Tool Calling)
- 외부 API, 데이터베이스, 기타 시스템과 상호작용하여 정보를 얻거나 작업을 수행하는 기술
- 메모리 및 컨텍스트 관리
- 장기/단기 메모리를 통해 지속적인 학습 및 상황 인식을 유지하는 기술
- 오케스트레이션 (Orchestration)
- 전체 작업 흐름을 제어하고 관리하여 목표 달성까지 이끄는 기술
- 요청 목적을 해석하고,
- 어떤 도구를 어떤 순서로 사용할지 계획하고,
- 상태를 유지하며 흐름을 제어함
- 전체 작업 흐름을 제어하고 관리하여 목표 달성까지 이끄는 기술
p5. AI 에이전트의 핵심 요소기술
오케스트레이션 패턴 및 프레임워크
- Chain(체인) 기반 오케스트레이션
- 미리 정의된 고정된 순서로 일련의 작업(프롬프트, 도구 호출 등)을 순차적으로 실행
- 선형적인 흐름에 적합
- 장단점: 구현이 단순하고 예측 가능성이 높으나, 유연성이 떨어지며 동적인 상황 변화에 대처하기 어려움
- 프레임워크: LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
- Agent(에이전트) 기반 오케스트레이션
- LLM이 스스로 추론(Reasoning)하고 계획(Planning)하여 동적으로 다음 행동(Action)을 결정하는 방식으로
ReAct (Reasoning and Acting) 패턴이 대표적 - 높은 자율성과 유연성을 가지며, 복잡하고 예측 불가능한 문제 해결에 적합하나,
비결정적 특성으로 인해 결과의 일관성이 떨어질 수 있음 - 프레임워크: LangChain의 AgentExecutor
- LLM이 스스로 추론(Reasoning)하고 계획(Planning)하여 동적으로 다음 행동(Action)을 결정하는 방식으로
- Graph(그래프) 기반 오케스트레이션
- 작업 흐름을 노드(상태 또는 행동)와 엣지(전환 조건)로 구성된 방향성 그래프로 정의
- 체인 방식보다 유연하고 에이전트 방식보다 흐름 제어가 명시적이어서,
복잡한 워크플로우를 안정적으로 구축 가능 - Reflection(반성)과 Loop(반복) 구현에 매우 강력
- 프레임워크: LangGraph, Microsoft Autogen (멀티 에이전트 협업)
p6. Agentic RAG
Agentic RAG 핵심 구성요소
- Query Analysis
- 사용자의 질문의 의도, 복잡도, 필요 정보를 파악
- Planning (계획 수립)
- 쿼리 분석 결과를 바탕으로 실행 계획을 수립
- 계획 수립 전략
- 선형 계획: 간단한 질문에 적합
- 분기 계획 (Branching Planning): 조건부 실행이 필요한 경우
- 병렬 계획: 독립적인 여러 정보 수집
- Agentic RAG의 핵심 패턴인 ReAct 패턴 활용
- Retrieval (검색)
- 적응형 검색 (Adaptive Retrieval)
- 하이브리드 검색 (Hybrid Search)
- 다단계 검색 (Multi-hop Retrieval)
- Self-Reflection (자기 성찰)
- 수집한 정보의 품질과 충분성을 평가
- 관련성(검색결과가 질문과 관련있는 정도),
완전성(정보가 충분한지),
신뢰성(정보 출처와 신뢰성)
- Tool Use (도구 사용): 다양한 도구 통합
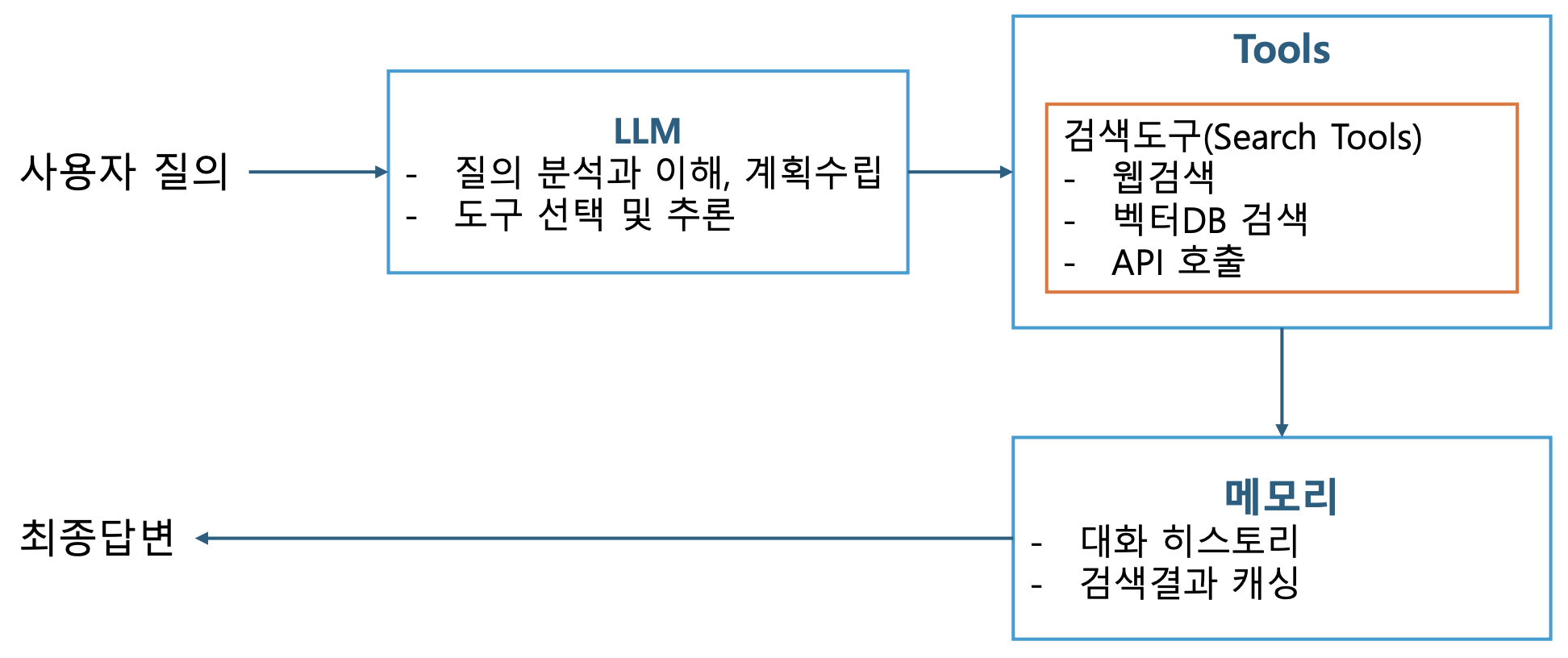
p7. Agentic RAG의 사고 과정
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# 의사 코드로 본 Agentic RAG 프로세스
def agentic_rag(query):
# 1. 질문 분석
analysis = analyze_query(query)
# "이 질문은 최신 정보가 필요하고, 수치 비교가 포함"
# 2. 전략 수립
strategy = plan_strategy(analysis)
# "먼저 최신 데이터를 검색하고, 그 다음 계산기를 사용"
# 3. 단계별 실행
for step in strategy:
if step.type == "search":
results = search(step.query)
# 4. 결과 평가
if not is_sufficient(results):
# 검색 쿼리 수정 후 재시도
results = search(refine_query(step.query))
elif step.type == "calculate":
results = calculator(step.expression)
# 5. 충분한지 판단
if has_enough_info():
break
# 6. 최종 답변 생성
return generate_answer(query, collected_info)
p8. Planning: ReAct 패턴 활용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
class ReActPlanner:
def __init__(self, llm):
self.llm = llm
def plan_next_action(self, query, history, observations):
prompt = f"""
현재 상황:
질문: {query}
지금까지의 행동: {history}
관찰 결과: {observations}
다음에 무엇을 해야 할까요?
Thought: [추론 과정]
Action: [search/calculate/aggregate/answer]
Action Input: [구체적 입력]
"""
response = self.llm.generate(prompt)
return self.parse_react_response(response)
def execute_plan(self, query):
history = []
observations = []
max_iterations = 10
for i in range(max_iterations):
# 다음 행동 결정
action = self.plan_next_action(
query, history, observations
)
if action.type == "answer":
# 충분한 정보 확보
return action.content
# 행동 실행
result = self.execute_action(action)
# 기록
history.append(action)
observations.append(result)
return "최대 반복 횟수 도달"
p9. Retrieval (검색) – Adaptive Retrieval
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
class AdaptiveRetriever:
def retrieve(self, query, context=None):
# 첫 검색
results = self.initial_search(query)
# 결과 평가
quality = self.evaluate_results(results, query)
if quality < THRESHOLD:
# 검색 전략 변경
if quality.issue == "too_broad":
# 더 구체적으로
results = self.search(self.make_specific(query))
elif quality.issue == "outdated":
# 시간 제약 추가
results = self.search(
f"{query} 2024",
filter={"date": "last_6_months"}
)
elif quality.issue == "no_results":
# 쿼리 완화
results = self.search(self.expand_query(query))
return results
p10. Retrieval (검색) – 하이브리드 검색 (Hybrid Search)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
class HybridSearcher:
def __init__(self, vector_db, bm25_index):
self.vector_db = vector_db
self.bm25_index = bm25_index
def search(self, query, alpha=0.5):
# 의미 검색 (Vector Search)
semantic_results = self.vector_db.search(query, top_k=20)
# 키워드 검색 (BM25)
keyword_results = self.bm25_index.search(query, top_k=20)
# 점수 결합
combined = self.reciprocal_rank_fusion(
semantic_results,
keyword_results,
alpha=alpha
)
return combined[:10] # Top 10 반환
def reciprocal_rank_fusion(self, results1, results2, alpha=0.5):
"""RRF 알고리즘으로 결과 결합"""
scores = {}
k = 60 # RRF 상수
for rank, doc in enumerate(results1):
scores[doc.id] = scores.get(doc.id, 0) + alpha / (k + rank + 1)
for rank, doc in enumerate(results2):
scores[doc.id] = scores.get(doc.id, 0) + (1 - alpha) / (k + rank + 1)
return sorted(scores.items(),
key=lambda x: x[1],
reverse=True)
p11. Retrieval (검색) – 다단계 검색 (Multi-hop Retrieval)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
class MultiHopRetriever:
def retrieve(self, query, max_hops=3):
results = []
current_query = query
for hop in range(max_hops):
# 현재 쿼리로 검색
hop_results = self.search(current_query)
results.extend(hop_results)
# 다음 검색이 필요한지 판단
need_more = self.assess_information_gap(
query, results
)
if not need_more:
break
# 다음 쿼리 생성
current_query = self.generate_followup_query(
query, results
)
return self.deduplicate_and_rank(results)
p12. 검색 에이전트
p13. 검색 에이전트
필수 구성요소
- LLM
- OpenAI GPT-4, …
- Anthropic Claude
- Google PaLM
- 오픈소스 모델(Llama, Mistral 등)
- 도구
- 검색도구
- SerpAPI: Google 검색
- DuckDuckGo: 프라이버시 중심 검색
- Wikipedia: 백과사전 정보
- ArXiv: 학술 논문 검색
- 벡터 저장소
- 유틸리티 도구
- Calculator: 수학 계산
- Python REPL: 코드 실행
- Requests: HTTP 요청
- 검색도구
- 메모리
- ConversationBufferMemory: 전체 대화 저장
- ConversationSummaryMemory: 요약 저장
- ConversationBufferWindowMemory: 최근 N개 메시지만 저장
- VectorStoreMemory: 벡터 기반 관련 메모리 검색
p14. LangChain을 이용한 검색 에이전트
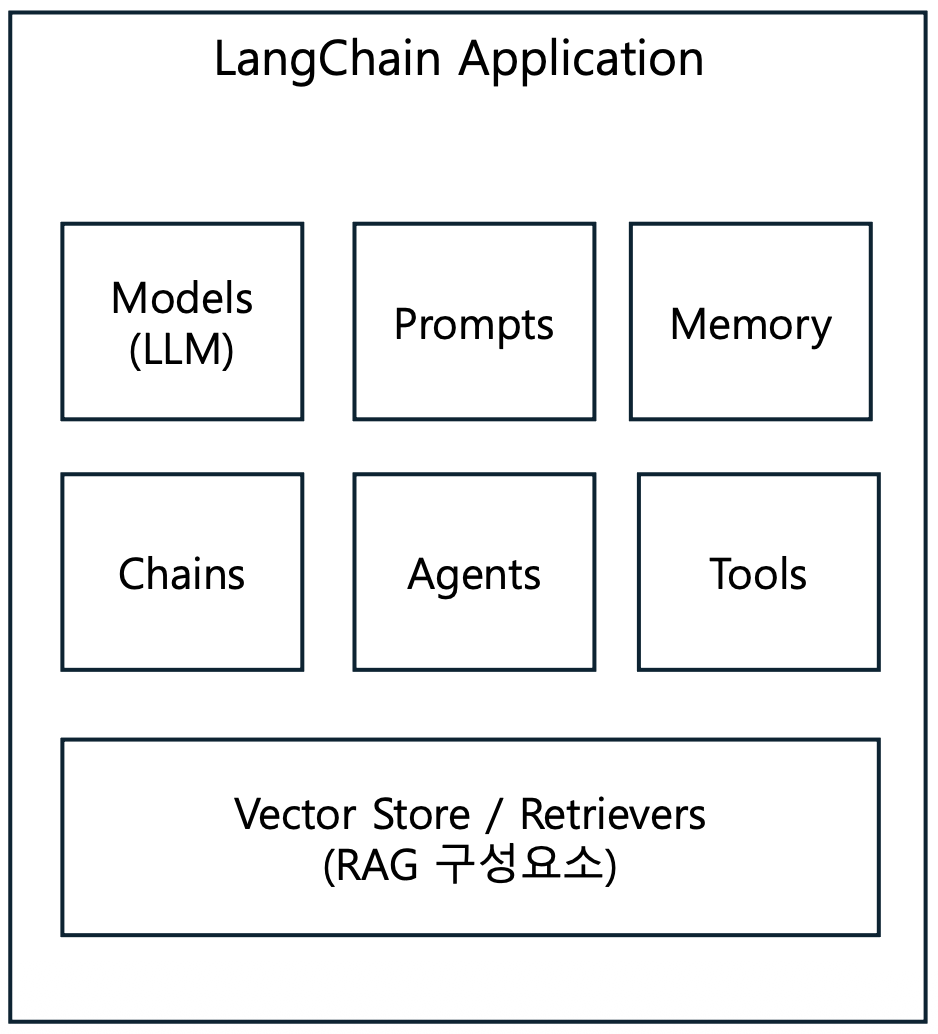
- LangChain ?
- LangChain은 대규모 언어 모델(LLM)을 활용한 애플리케이션 개발을 위한 프레임워크
- 핵심 기능
- 프롬프트 관리 및 최적화
- 체인(Chain) 구성을 통한 복잡한 워크플로우 구현
- 데이터 소스 연결 및 통합
- 에이전트를 통한 자율적 작업 수행
- 메모리 관리
p15. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
- LangChain 정의
- LangChain은 대규모 언어 모델(LLM)을 활용한 애플리케이션을 쉽게 개발할 수 있도록 돕는 오픈소스 프레임워크
- LangChain의 핵심 가치
- 모듈화 (Modularity)
- 재사용 가능한 컴포넌트들로 구성 (LLM + 프롬프트 + 메모리 + 도구)
- 체인 (Chaining)
- 여러 작업을 순차적으로 연결 (입력 → 처리1 → 처리2 → 처리3 → 출력)
- 에이전트 (Agents)
- LLM이 스스로 판단하고 도구를 선택
- 모듈화 (Modularity)
p16. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
- 구성요소
- Agent: 의사 결정을 담당하는 핵심 컴포넌트
- Tools: 에이전트가 사용할 수 있는 기능들의 집합
- Toolkits: 관련된 도구들의 그룹
- AgentExecutor: 에이전트의 실행을 관리하는 컴포넌트
- 에이전트의 작동 방식
- 입력 수신: 사용자로부터 작업이나 질문 입력
- 계획 수립: 주어진 작업을 완료하기 위한 단계별 계획을 수립
- 도구 선택: 각 단계에 적합한 도구를 선택
- 실행: 선택한 도구를 사용하여 작업을 수행
- 결과 평가: 수행 결과를 평가하고 필요 시 계획을 조정
- 출력 생성: 최종 결과와 답변을 사용자에게 제공
p17. LangChain을 이용한 검색 에이전트
LangChain 개발환경 설정
- 필요 패키지 설치
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
# 기본 LangChain 설치 pip install langchain langchain-community langchain-openai # 검색 도구 pip install google-search-results duckduckgo-search wikipedia # 벡터 저장소 pip install chromadb faiss-cpu # 유틸리티 pip install python-dotenv requests beautifulsoup4
- 환경변수 설정
1 2 3
# .env 파일 생성 OPENAI_API_KEY=your_openai_api_key SERPAPI_API_KEY=your_serpapi_key
p18. LangChain을 이용한 검색 에이전트
- 기본 임포트
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent, Tool, AgentType from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory from langchain.prompts import MessagesPlaceholder from dotenv import load_dotenv import os # 환경 변수 로드 load_dotenv()
p19. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
LangChain 구성요소
- Models: LLM과 상호작용하는 인터페이스
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
# OpenAI from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4", temperature=0.7) # Anthropic Claude from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic llm = ChatAnthropic(model="claude-3-opus-20240229") # Google from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-pro") # Local models (Ollama) from langchain_community.llms import Ollama llm = Ollama(model="llama2") # 기본 사용 response = llm.invoke("한국의 수도는?") print(response.content) # "서울입니다" # 스트리밍 for chunk in llm.stream("긴 이야기를 들려줘"): print(chunk.content, end="", flush=True) # 배치 처리 questions = ["1+1은?", "서울의 인구는?", "파이썬이란?"] responses = llm.batch(questions)
p20. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
LangChain 구성요소
- Prompts (프롬프트): LLM에게 전달하는 지시사항 템플릿
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate # 기본 템플릿 template = """ 당신은 {role} 전문가입니다. 다음 질문에 {style} 스타일로 답변해주세요. 질문: {question} 답변: """ prompt = PromptTemplate( input_variables=["role", "style", "question"], template=template ) # 사용 formatted = prompt.format( role="AI", style="친절하고 상세한", question="머신러닝이란?" )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([ ("system", "당신은 {domain} 전문가입니다."), ("human", "안녕하세요!"), ("ai", "안녕하세요! 무엇을 도와드릴까요?"), ("human", "{question}") ]) messages = chat_prompt.format_messages( domain="프로그래밍", question="파이썬 클래스 설명해줘" )
p22. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
LangChain 구성요소
Memory: 대화 기록 및 컨텍스트 유지
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
# ConversationBufferMemory (전체 기록) from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory memory = ConversationBufferMemory() # 대화 저장 memory.save_context( {"input": "안녕"}, {"output": "안녕하세요!"} ) memory.save_context( {"input": "내 이름은 철수야"}, {"output": "반갑습니다, 철수님!"} ) # 기록 조회 print(memory.load_memory_variables({}))
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
# ConversationBufferWindowMemory (최근 N개만) from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferWindowMemory # 최근 2개 대화만 기억 memory = ConversationBufferWindowMemory(k=2) memory.save_context({"input": "1"}, {"output": "1"}) memory.save_context({"input": "2"}, {"output": "2"}) memory.save_context({"input": "3"}, {"output": "3"}) memory.save_context({"input": "4"}, {"output": "4"}) # 최근 2개만 로드됨 print(memory.load_memory_variables({}))
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
# ConversationSummaryMemory (요약) from langchain.memory import ConversationSummaryMemory # 긴 대화를 요약하여 저장 memory = ConversationSummaryMemory(llm=llm) # 긴 대화 long_conversation = """ Human: 저는 서울에 사는 개발자입니다. AI: 반갑습니다! Human: 파이썬을 주로 사용하고 AI에 관심이 많아요. AI: 좋은 선택이네요! """ # 요약되어 저장 # "서울 거주 개발자, 파이썬 사용, AI 관심"
p23. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
LangChain 구성요소
- Chains: 여러 컴포넌트를 연결하여 작업 흐름 구성
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
# 기본체인 from langchain.chains import LLMChain chain = LLMChain( llm=llm, prompt=prompt, memory=memory ) # 실행 result = chain.run(question="파이썬이란?")
p24. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
LangChain 구성요소
Chains: 여러 컴포넌트를 연결하여 작업 흐름 구성
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
# Sequential Chain from langchain.chains import SimpleSequentialChain # 체인 1: 주제 생성 chain1 = LLMChain( llm=llm, prompt=PromptTemplate( input_variables=["product"], template="다음 제품의 광고 문구를 만들어줘: {product}" ) ) # 체인 2: 번역 chain2 = LLMChain( llm=llm, prompt=PromptTemplate( input_variables=["ad_copy"], template="다음 문구를 영어로 번역해줘: {ad_copy}" ) ) # 연결 overall_chain = SimpleSequentialChain( chains=[chain1, chain2], verbose=True ) # 실행 result = overall_chain.run("스마트폰") # 1. "혁신적인 기술, 당신의 손 안에" # 2. "Innovative technology in your hands"
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
# Router Chain from langchain.chains.router import MultiPromptChain # 물리학 프롬프트 physics_template = """당신은 물리학자입니다. 질문: {input}""" # 수학 프롬프트 math_template = """당신은 수학자입니다. 질문: {input}""" # 라우터 설정 prompt_infos = [ {"name": "physics", "description": "물리학 질문", "template": physics_template}, {"name": "math", "description": "수학 질문", "template": math_template} ] # 질문에 따라 자동으로 적절한 전문가 선택 chain = MultiPromptChain(...)
p25. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
LangChain 구성요소
Agents: LLM이 스스로 도구를 선택하고 사용
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent, Tool from langchain.agents import AgentType # 도구 정의 def search(query): return f"{query}에 대한 검색 결과" def calculate(expression): return eval(expression) tools = [ Tool( name="검색", func=search, description="정보를 검색할 때 사용. 입력: 검색어" ), Tool( name="계산기", func=calculate, description="수학 계산을 할 때 사용. 입력: 수식" ) ] # 에이전트 초기화 agent = initialize_agent( tools=tools, llm=llm, agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION, verbose=True ) # 실행 result = agent.run("2023년 GDP 성장률에 10을 곱해줘") result = agent.invoke({"input": "2023년 GDP 성장률에 10을 곱해줘"}) # 에이전트 사고 과정: # 1. "GDP 성장률을 알아야 해" → 검색 도구 사용 # 2. "검색 결과: 2.3%" 획득 # 3. "2.3 * 10을 계산해야 해" → 계산기 사용 # 4. "결과: 23" → 최종 답변 생성 print(result) # 출력: 딕셔너리 (상세 정보 포함)
initialize_agent():
LLM, Tools, 에이전트 유형(Agent Type) 등의 매개변수를 바탕으로
완성된 형태의 AgentExecutor를 자동 설정하고 초기화AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION:
프롬프트에 기반한 리액트(ReAct) 방식 에이전트
p26. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
LangChain 구성요소
- Agent를 실행하는 방법
- agent.run(query)
- LangChain의 구버전 실행 메서드
- 에이전트 실행 최종답변만 반환
- 중간과정 확인불가, 메타데이터 접근 불가
- agent.invoke(input)
- LangChain의 현대적 표준 실행 메서드
- 상세한 실행 정보를 딕셔너리로 반환
- 프로덕션 코드 생성 시 사용
- 중간과정 확인 가능
- agent.stream(input)
- 실시간 스트리밍 필요 시 사용
- agent.batch(inputs)
- 배치처리
- agent.ainvoke(input)
- 비동기 실행
- AgentExecutor
1 2 3
# 실시간으로 토큰 스트리밍 for chunk in agent.stream({"input": "질문"}): print(chunk, end="", flush=True)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
# 여러 질문을 한 번에 처리 questions = [ {"input": "질문1"}, {"input": "질문2"}, {"input": "질문3"} ] results = agent.batch(questions) for result in results: print(result["output"])
1 2 3 4 5 6
# 비동기 실행 async def main(): result = await agent.ainvoke({"input": "질문"}) print(result["output"]) asyncio.run(main())
- agent.run(query)
p27. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
LangChain 구성요소
- AgentExecutor
- 실제 에이전트 실행 관리 클래스
initialize_agent()가 내부적으로 생성하는 객체- 강력하고 세밀한 제어가 가능
- 커스텀 오류처리
- 복잡한 메모리 관리
- 고급 설정(타임아웃, 반복제한 등)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_openai_functions_agent from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder # 1. 프롬프트 정의 prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([ ("system", "당신은 유능한 AI 어시스턴트입니다."), ("human", "{input}"), MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="agent_scratchpad") ]) # 2. 에이전트 생성 agent = create_openai_functions_agent( llm=llm, tools=tools, prompt=prompt ) # 3. AgentExecutor 생성 (실행 엔진) agent_executor = AgentExecutor( agent=agent, # 에이전트 객체 tools=tools, # 도구 리스트 verbose=True, # 실행 과정 출력 max_iterations=10, # 최대 반복 횟수 max_execution_time=60, # 최대 실행 시간(초) early_stopping_method="generate", # "force" 또는 "generate" handle_parsing_errors=True ) # 4. 실행 result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": "질문"})
p28. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent, AgentExecutor
from langchain.agents import create_openai_functions_agent
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
tools = [...] # 도구 정의
# =========================================
# 방법 1: agent.run() (레거시)
# =========================================
agent1 = initialize_agent(
tools=tools,
llm=llm,
agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION
)
result1 = agent1.run("파이썬이란?")
print(type(result1)) # <class 'str'>
print(result1) # "파이썬은..."
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# =========================================
# 방법 2: agent.invoke() (권장)
# =========================================
agent2 = initialize_agent(
tools=tools,
llm=llm,
agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
return_intermediate_steps=True
)
result2 = agent2.invoke({"input": "파이썬이란?"})
print(type(result2)) # <class 'dict'>
print(result2["output"]) # "파이썬은..."
print(result2["intermediate_steps"]) # 중간 과정
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# =========================================
# 방법 3: AgentExecutor (고급)
# =========================================
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "당신은 유능한 어시스턴트입니다."),
("human", "{input}"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="agent_scratchpad")
])
agent_core = create_openai_functions_agent(
llm=llm,
tools=tools,
prompt=prompt
)
agent3 = AgentExecutor(
agent=agent_core,
tools=tools,
verbose=True,
max_iterations=10,
return_intermediate_steps=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True
)
result3 = agent3.invoke({"input": "파이썬이란?"})
print(type(result3)) # <class 'dict'>
print(result3["output"])
print(result3["intermediate_steps"])
p29. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_openai_functions_agent
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
# 메모리
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key="chat_history",
return_messages=True
)
# 프롬프트
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "당신은 친절한 AI 어시스턴트입니다."),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="agent_scratchpad")
])
# 에이전트 생성
agent = create_openai_functions_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
# AgentExecutor 생성
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
memory=memory,
verbose=True,
max_iterations=10,
return_intermediate_steps=True
)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 대화 시작
print("챗봇: 안녕하세요! 무엇을 도와드릴까요?")
while True:
user_input = input("사용자: ")
if user_input.lower() in ['quit', 'exit', '종료']:
print("챗봇: 안녕히 가세요!")
break
result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": user_input})
print(f"챗봇: {result['output']}\n")
p30. LangChain을 이용한 Agent 구현 예시
p31. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
Agent 프롬프트 생성
- chat_history: 이전 대화 내용을 저장하는 변수 (멀티턴을 지원하지 않는다면 생략 가능)
- agent_scratchpad: 에이전트가 임시로 저장하는 변수
- input: 사용자의 입력
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
# 프롬프트 생성
# 프롬프트는 에이전트에게 모델이 수행할 작업을 설명하는 텍스트를 제공합니다. (도구의 이름과 역할을 입력)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
"You are a helpful assistant. "
"Make sure to use the `search_news` tool for searching keyword related news.",
),
("placeholder", "{chat_history}"),
("human", "{input}"),
("placeholder", "{agent_scratchpad}"),
]
)
p32. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
Agent Calling Tools
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 도구 생성
@tool
def search_google_news(query: str) -> str:
"""
구글에서 뉴스를 검색합니다.
Args: query: 검색할 키워드
Returns: 검색 결과 URL 리스트 (문자열)
"""
try:
# 뉴스 검색을 위해 쿼리 수정
news_query = f"{query} site:news.google.com OR site:naver.com/news "
# 구글 검색 수행 (최대 5개 결과)
search_results = []
for idx, url in enumerate(search(news_query, num_results=5)):
search_results.append(f"{idx+1}. {url}")
if not search_results:
return "검색 결과가 없습니다."
return "\n".join(search_results)
except Exception as e:
return f"검색 중 오류 발생: {str(e)}"
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
def get_article_content(url: str) -> str:
"""
뉴스 기사 URL에서 제목 추출합니다.
Args: url: 뉴스 기사 URL
Returns: 기사 제목
"""
try:
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36'
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=10)
response.encoding = 'utf-8'
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
# 제목 추출
title = soup.find('title')
title_text = title.get_text().strip() if title else "제목 없음"
return f"제목: {title_text}\n"
except Exception as e:
return f"기사 내용을 가져오는 중 오류 발생: {str(e)}"
1
2
# tools 정의
tools = [search_google_news, get_article_content]
p33. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
Agent Calling Tools
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
from langchain.tools import tool
from typing import List, Dict, Annotated
from langchain_teddynote.tools import GoogleNews
from langchain_experimental.utilities import PythonREPL
# 도구 생성
@tool
def search_news(query: str) -> List[Dict[str, str]]:
"""Search Google News by input keyword"""
news_tool = GoogleNews()
return news_tool.search_by_keyword(query, k=5)
# 도구 생성
@tool
def python_repl_tool(
code: Annotated[str, "The python code to execute to generate your chart."]
):
"""Use this to execute python code. If you want to see the output of a value,
you should print it out with `print(...)`. This is visible to the user."""
result = ""
try:
result = PythonREPL().run(code)
except BaseException as e:
print(f"Failed to execute. Error: {repr(e)}")
finally:
return result
1
2
# tools 정의
tools = [search_news, python_repl_tool]
p34. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
Agent 생성
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.agents import create_tool_calling_agent
# LLM 정의
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
# Agent 생성
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
p35. LangChain을 이용한 Agent
AgentExecutor: AgentExecutor는 도구를 사용하는 에이전트를 실행하는 클래스
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor
# AgentExecutor 생성
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
verbose=True,
max_iterations=10,
max_execution_time=10,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
)
# AgentExecutor 실행
result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": "AI 투자와 관련된 뉴스를 검색해 주세요."})
print("Agent 실행 결과:")
print(result["output"])
주요 속성
- agent: 실행 루프의 각 단계에서 계획을 생성하고 행동을 결정하는 에이전트
- tools: 에이전트가 사용할 수 있는 유효한 도구 목록
- return_intermediate_steps: 최종 출력과 함께 에이전트의 중간 단계 경로를 반환할지 여부
- max_iterations: 실행 루프를 종료하기 전 최대 단계 수
- max_execution_time: 실행 루프에 소요될 수 있는 최대 시간
- early_stopping_method: 에이전트가 AgentFinish를 반환하지 않을 때 사용한 조기 종료 방법
- “force”: 시간 또는 반복 제한에 도달했음을 알리는 문자열을 반환
- “generate”: 에이전트의 LLM 체인을 마지막으로 호출해 이전 단계에 따라 최종 답변을 생성
- handle_parsing_errors: 에이전트의 출력 파싱 중 발생한 오류를 처리하는 방법
- trim_intermediate_steps: 중간 단계를 트리밍하는 방법 (-1: 트리밍하지 않음, 또는 트리밍 함수)
주요 메서드
- invoke: 에이전트 실행
- stream: 최종 출력에 도달하는 데 필요한 단계를 스트리밍
p36. LangGraph를 이용한 AgentRAG 개발
LangGraph
- LLM 기반 애플리케이션을 그래프 구조로 설계하고 실행할 수 있는 프레임워크
- LangChain 위에 구축되어 있으며, 복잡한 에이전트 워크플로우를 상태 기반 그래프로 표현
왜 LangGraph?
LangChain의 한계점
- 블랙박스: 내부 동작을 제어하기 어려움
- 제한적 흐름: 선형적 실행만 가능
- 복잡한 로직 구현 어려움
- 디버깅 어려움
- 순환 흐름(Cycle) 불가
LangGraph의 장점
- 명시적 제어: 각 단계를 명확히 정의
- 복잡한 흐름: 조건부 분기, 병렬 처리, 순환
- 상태 관리: 중간 상태를 추적하고 수정 가능
- 디버깅 용이: 각 단계별 결과 확인 가능
- 유연성: 사람 개입(Human-in-the-loop) 가능
p37. LangGraph를 이용한 AgentRAG 개발
LangGraph의 핵심 기능
- 그래프 기반 워크플로우 (Graph-Based Workflow)
- 노드(Node)와 엣지(Edge)
- 각 작업 단계(LLM 호출, 도구 사용, 일반 함수 등)를 ‘노드’로 정의하고,
노드 간의 실행 순서를 ‘엣지’로 연결
- 각 작업 단계(LLM 호출, 도구 사용, 일반 함수 등)를 ‘노드’로 정의하고,
- 순환(Cycles) 지원
- 기존 LangChain의 순차적 체인 구조와 달리, 그래프 내에서 루프(반복)를 생성 가능
- 에이전트의 지속적인 추론 및 자기개선 루프, 재시도 로직 구현 가능
- 노드(Node)와 엣지(Edge)
- 세밀한 제어 흐름 (Fine-grained Control Flow)
- 조건부 엣지 (Conditional Edges)
- 특정 조건(예: LLM의 출력 결과)에 따라 다음 실행할 노드를 동적으로 결정
- 복잡한 분기 로직(if/else) 구현 가능
- 상태 관리 (State Management)
- TypedDict 등을 사용해 워크플로우 전반에 걸친 상태(기억)를 유지하고 업데이트
- 여러 단계의 상호작용에서 정보를 잃지 않고 전달
- 조건부 엣지 (Conditional Edges)
- 고급 에이전트 기능 지원
- 지속성 및 내결함성 (Persistence & Fault Tolerance)
- 에이전트의 현재 상태를 저장하고 필요 시 중단된 지점부터 다시 시작 가능
- Human-in-the-Loop (HITL)
- 특정 노드에서 실행을 일시 중지하고 인간의 검토나 입력을 요청할 수 있는 기능 지원
- 멀티 에이전트 시스템
- 여러 개의 에이전트가 협력하여 작업을 수행하는 복잡한 시스템을 구축하기 용이
- 지속성 및 내결함성 (Persistence & Fault Tolerance)
p38. LangGraph를 이용한 AgentRAG 개발
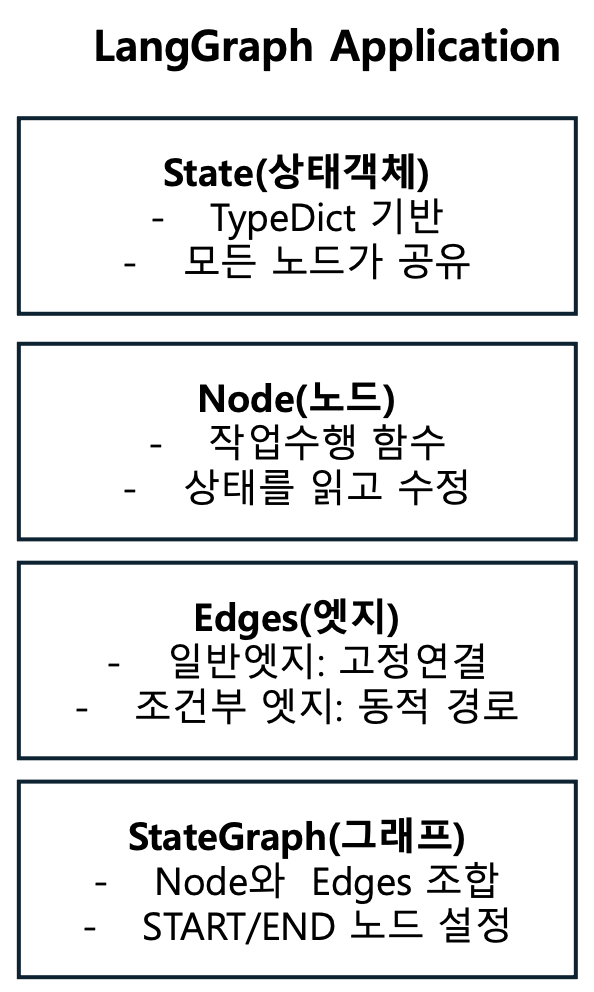
LangGraph의 핵심 구성 요소
- State (상태): 모든 노드가 공유하는 데이터 구조
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
from typing import TypedDict, Annotated, Sequence
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage
import operator
class AgentState(TypedDict):
"""에이전트의 상태를 정의"""
# 대화 메시지 (누적)
messages: Annotated[Sequence[BaseMessage], operator.add]
current_step: str # 현재 단계
retrieved_docs: list # 검색된 문서
answer: str # 최종 답변
iteration: int # 반복 횟수
Python의 TypedDict를 상속받아 정의
- 상태가 정해진 키와 타입을 갖도록 강제
- 코드의 안정성 유지
Annotated: 상태 업데이트 방식 지정
- operator.add: 기존 값에 추가 (리스트, 문자열)
- 기본: 덮어쓰기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 초기 상태
state = {
"messages": [],
"current_step": "start",
"iteration": 0
}
# 노드 1 실행 후
state = {
"messages": [HumanMessage("안녕")], # 추가됨
"current_step": "검색", # 덮어씀
"iteration": 1 # 증가
}
# 노드 2 실행 후
state = {
"messages": [
HumanMessage("안녕"),
AIMessage("안녕하세요") # 추가
],
"current_step": "답변",
"iteration": 2
}
p39. LangGraph를 이용한 AgentRAG 개발
LangGraph의 핵심 구성 요소
- Nodes (노드): 실제 작업을 수행하는 함수
기본 노드 구조
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
def my_node(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""
노드 함수
Args:
state: 현재 상태
Returns:
업데이트된 상태 (딕셔너리 형태)
"""
# 1. 상태에서 필요한 정보 읽기
current_step = state["current_step"]
messages = state["messages"]
# 2. 작업 수행
result = do_something(messages)
# 3. 상태 업데이트 반환
return {
"messages": [AIMessage(result)],
"current_step": "next_step"
}
p40. LangGraph를 이용한 AgentRAG 개발
검색 노드 예시
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, AIMessage
def search_node(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""문서 검색 노드"""
# 마지막 사용자 질문 추출
messages = state["messages"]
question = messages[-1].content
# 벡터 DB에서 검색
retriever = vector_store.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 3})
docs = retriever.get_relevant_documents(question)
# 상태 업데이트
return {
"retrieved_docs": docs,
"current_step": "검색완료",
"messages": [AIMessage(f"{len(docs)}개 문서 검색 완료")]
}
답변 노드 예시
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
def generate_node(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""답변 생성 노드"""
messages = state["messages"]
docs = state["retrieved_docs"]
# 문서 내용 결합
context = "\n\n".join([doc.page_content for doc in docs])
# 프롬프트 구성
prompt = f"""
다음 문서를 참고하여 질문에 답변하세요.
문서:
{context}
질문: {messages[0].content}
답변:
"""
# LLM 호출
response = llm.invoke(prompt)
return {
"answer": response.content,
"current_step": "완료",
"messages": [AIMessage(response.content)]
}
p41. LangGraph를 이용한 AgentRAG 개발
LangGraph의 핵심 구성 요소
- Edges (엣지): 노드 간 연결을 정의
일반 엣지 (Normal Edge)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 항상 A → B로 이동
graph.add_edge("A", "B")
workflow = StateGraph(AgentState)
workflow.add_node("검색", search_node)
workflow.add_node("생성", generate_node)
# 검색 후 항상 생성으로 이동
workflow.add_edge("검색", "생성")
조건부 엣지 (Conditional Edge)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
def decide_next(state: AgentState) -> str:
"""다음 노드 결정"""
if state["iteration"] > 3:
return "종료"
elif state["retrieved_docs"]:
return "생성"
else:
return "검색"
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"평가", # 출발 노드
decide_next, # 결정 함수
{
"검색": "search_node",
"생성": "generate_node",
"종료": END
}
)
p42. LangGraph를 이용한 AgentRAG 개발
LangGraph의 핵심 구성 요소
- StateGraph (상태 그래프)
- 노드와 엣지를 조합한 실행 가능한 그래프
특수 노드: START와 END
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
from langgraph.graph import START, END
# START: 진입점 (가상 노드)
workflow.set_entry_point("first_node")
# 또는
workflow.add_edge(START, "first_node")
# END: 종료점 (가상 노드)
workflow.add_edge("last_node", END)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
# 1. 그래프 생성
Workflow = StateGraph(AgentState)
# 2. 노드 추가
Workflow.add_node("node1", node1_function)
Workflow.add_node("node2", node2_function)
Workflow.add_node("node3", node3_function)
# 3. 엣지 추가
workflow.add_edge("node1", "node2")
workflow.add_conditional_edges("node2", decide_function, {...})
# 4. 시작점 설정
workflow.set_entry_point("node1")
# 5. 종료점 설정
workflow.add_edge("node3", END)
# 6. 컴파일
app = workflow.compile()
# 7. 실행
result = app.invoke({"messages": [HumanMessage("안녕")]})
p43. LangGraph를 이용한 AgentRAG 개발
LangGraph의 주요 기능
- 순환(Cycles): 동일 노드를 반복 실행
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
def improve_node(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""답변을 개선하는 노드"""
iteration = state.get("iteration", 0)
answer = state.get("answer", "")
if iteration >= 3:
# 최대 반복 도달
return {"current_step": "완료"}
# 답변 개선
improved = llm.invoke(f"다음 답변을 더 나아지게 개선: {answer}")
return {
"answer": improved.content,
"iteration": iteration + 1,
"current_step": "개선중"
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
def should_continue(state: AgentState) -> str:
"""계속할지 결정"""
if state["iteration"] >= 3:
return "완료"
else:
return "개선"
# 순환 그래프
workflow.add_node("개선", improve_node)
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"개선",
should_continue,
{
"개선": "개선", # 자기 자신으로 순환
"완료": END
}
)
p44. LangGraph를 이용한 AgentRAG 개발
LangGraph의 주요 기능
- 병렬 처리 (Parallel Execution)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
def search_web(state):
"""웹 검색"""
return {"web_results": "..."}
def search_db(state):
"""DB 검색"""
return {"db_results": "..."}
def search_vector(state):
"""벡터 DB 검색"""
return {"vector_results": "..."}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 병렬 실행
workflow.add_node("웹검색", search_web)
workflow.add_node("DB검색", search_db)
workflow.add_node("벡터검색", search_vector)
# 모두 병렬로 실행
workflow.add_edge(START, "웹검색")
workflow.add_edge(START, "DB검색")
workflow.add_edge(START, "벡터검색")
# 결과 통합
workflow.add_node("통합", combine_results)
workflow.add_edge("웹검색", "통합")
workflow.add_edge("DB검색", "통합")
workflow.add_edge("벡터검색", "통합")
p45. LangGraph를 이용한 AgentRAG 개발
LangGraph의 주요 기능
- 체크포인트 (Checkpointing): 중간 상태 저장 및 복구
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
from langgraph.checkpoint.sqlite import SqliteSaver
# 영구 저장소
memory = SqliteSaver.from_conn_string("./checkpoints.db")
app = workflow.compile(checkpointer=memory)
# 실행 (자동 저장)
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "conversation-1"}}
result = app.invoke(initial_state, config)
# 나중에 이어서 실행
result = app.invoke({"messages": [HumanMessage("계속")]}, config)
# 특정 시점으로 되돌리기
state_history = app.get_state_history(config)
for state in state_history:
print(state)
p47. LangChain을 이용한 검색 에이전트 핵심 기능 구현 예시
간단한 검색 에이전트
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
from langchain.agents import load_tools, initialize_agent, AgentType
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
# LLM 초기화
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4",
temperature=0
)
# 도구 로드
tools = load_tools(
["serpapi", "llm-math"],
llm=llm
)
# 에이전트 초기화
agent = initialize_agent(
tools=tools,
llm=llm,
agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
verbose=True
)
# 실행
response = agent.run(
"2024년 노벨 물리학상 수상자는 누구이며, 그들의 주요 업적은 무엇인가요?"
)
print(response)
p48. LangChain을 이용한 검색 에이전트 핵심 기능 구현 예시
커스텀 검색 도구 생성
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
from langchain.tools import Tool
from langchain.utilities import DuckDuckGoSearchAPIWrapper
# DuckDuckGo 검색 래퍼
search = DuckDuckGoSearchAPIWrapper()
# 커스텀 도구 정의
search_tool = Tool(
name="웹검색",
func=search.run,
description="최신 정보나 실시간 데이터가 필요할 때 유용합니다. "
"뉴스, 날씨, 최신 이벤트 등을 검색할 수 있습니다."
)
# Wikipedia 도구
from langchain.utilities import WikipediaAPIWrapper
wikipedia = WikipediaAPIWrapper()
wiki_tool = Tool(
name="위키피디아",
func=wikipedia.run,
description="역사적 사실, 인물 정보, 개념 설명 등 "
"검증된 백과사전 정보가 필요할 때 사용합니다."
)
# 도구 리스트
tools = [search_tool, wiki_tool]
1
2
# llm 모델이 tool을 호출할 수 있도록 하려면 도구 바인딩
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
p49. LangChain을 이용한 검색 에이전트 핵심 기능 구현 예시
메모리를 포함한 에이전트
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.prompts import MessagesPlaceholder
# 메모리 초기화
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key="chat_history",
return_messages=True
)
# 에이전트 생성
agent = initialize_agent(
tools=tools,
llm=llm,
agent=AgentType.CHAT_CONVERSATIONAL_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
memory=memory,
verbose=True,
agent_kwargs={
"memory_prompts": [
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="chat_history")
],
"input_variables": ["input", "agent_scratchpad", "chat_history"]
}
)
# 대화형 실행
print(agent.run("파이썬이 언제 만들어졌나요?"))
print(agent.run("그 언어의 창시자는 누구인가요?")) # 이전 맥락 기억
p50. LangChain을 이용한 검색 에이전트 핵심 기능 구현 예시
벡터 저장소를 활용한 RAG 에이전트
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
# 문서 로드 및 분할
loader = TextLoader("knowledge_base.txt")
documents = loader.load()
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1000,
chunk_overlap=200
)
texts = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
# 벡터 저장소 생성
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=texts,
embedding=embeddings,
persist_directory="./chroma_db"
)
# 검색 도구 생성
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 3})
knowledge_tool = Tool(
name="지식베이스",
func=RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
retriever=retriever
).run,
description="내부 문서나 지식베이스에서 정보를 검색할 때 사용합니다."
)
p51. LangChain을 이용한 검색 에이전트 핵심 기능 구현 예시
커스텀 에이전트 타입
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
from langchain.agents import BaseSingleActionAgent
from langchain.schema import AgentAction, AgentFinish
class CustomSearchAgent(BaseSingleActionAgent):
"""커스텀 검색 에이전트"""
tools: list
llm: ChatOpenAI
def plan(self, intermediate_steps, **kwargs):
"""다음 행동 계획"""
# 커스텀 로직 구현
user_input = kwargs["input"]
# LLM을 사용한 의사결정
# …
return AgentAction(
tool="웹검색",
tool_input=user_input,
log="검색을 수행합니다."
)
@property
def input_keys(self):
return ["input"]
p52. LangChain을 이용한 검색 에이전트 핵심 기능 구현 예시
에이전트 체인 구성
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
from langchain.chains import SequentialChain, LLMChain
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
# 1단계: 질의 분석 체인
analysis_template = """
다음 질문을 분석하여 필요한 정보를 파악하세요:
질문: {question}
분석 결과:
"""
analysis_chain = LLMChain(
llm=llm,
prompt=PromptTemplate(template=analysis_template, input_variables=["question"]),
output_key="analysis"
)
# 2단계: 검색 전략 수립 체인
strategy_template = """
분석 결과를 바탕으로 검색 전략을 수립하세요:
분석: {analysis}
검색 전략:
"""
strategy_chain = LLMChain(
llm=llm,
prompt=PromptTemplate(template=strategy_template, input_variables=["analysis"]),
output_key="strategy"
)
# 순차 체인 구성
chain = SequentialChain(
chains=[analysis_chain, strategy_chain],
input_variables=["question"],
output_variables=["analysis", "strategy"],
verbose=True
)